Thinking about upgrading your home’s exterior? Insulated vinyl siding offers a compelling blend of aesthetics, energy efficiency, and long-term value. Unlike traditional vinyl, it incorporates an insulating layer, significantly impacting your home’s thermal performance and reducing energy bills. This guide dives deep into the material’s composition, installation, cost analysis, and design options, empowering you to make an informed decision.
We’ll explore the science behind its energy-saving capabilities, comparing it to other siding materials and highlighting the potential return on investment. We’ll also cover the practical aspects of installation, addressing common challenges and showcasing diverse design possibilities to help you achieve your dream home exterior.
Insulated Vinyl Siding
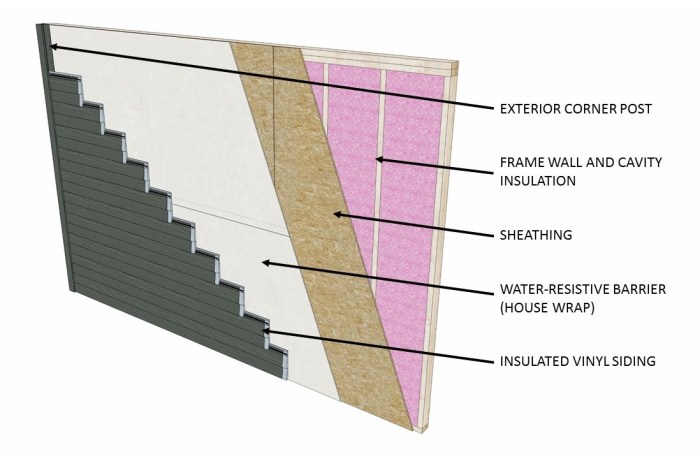
Insulated vinyl siding represents a significant advancement in exterior cladding, offering superior energy efficiency compared to traditional vinyl siding. Understanding its composition, manufacturing process, and performance characteristics is crucial for homeowners and builders seeking durable and cost-effective solutions. This deep dive will illuminate the key aspects of this increasingly popular building material.
Insulated Vinyl Siding: Layer Composition and Functions
Insulated vinyl siding isn’t just a single layer; it’s a composite material typically consisting of three distinct layers working in concert. The outer layer is a durable vinyl skin, providing weather resistance, color, and aesthetic appeal. This layer is UV-resistant and designed to withstand harsh weather conditions. The middle layer is the insulation core, usually made of rigid foam insulation like polyurethane or polyisocyanurate. This core is the key to the siding’s superior thermal performance, acting as a barrier against heat transfer. Finally, the inner layer is often a foam backing or a slightly textured surface designed for better adhesion to the wall sheathing and improved overall structural integrity. Each layer plays a vital role in the overall performance and longevity of the siding.
Composition’s Impact on Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
The inclusion of the insulating foam core is what sets insulated vinyl siding apart. This core significantly reduces heat transfer through the wall assembly, leading to lower energy consumption for heating and cooling. The R-value of the insulation core is a key indicator of its thermal resistance; higher R-values signify better insulation. For example, a siding with an R-value of 4 will offer significantly better insulation than traditional vinyl siding, which has virtually no R-value. This translates to tangible savings on energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
Material Properties: Insulated Vinyl Siding vs. Traditional Vinyl Siding
Compared to traditional vinyl siding, insulated vinyl siding boasts superior thermal performance, as previously discussed. However, it’s also generally heavier and may require more robust fastening. While both types are relatively low-maintenance, the added insulation layer in insulated vinyl siding might offer slightly enhanced resistance to impact damage. Traditional vinyl siding, being thinner and less substantial, is often more susceptible to dents and scratches. The cost is also a factor, with insulated vinyl siding typically being more expensive upfront. The long-term energy savings, however, often offset this initial cost difference.
Insulated Vinyl Siding Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process involves several key steps. First, the individual layers – the vinyl skin and the insulation core – are produced separately. The insulation core is often created using extrusion or molding techniques, depending on the specific foam type. Then, the vinyl skin is precisely formed and adhered to the insulation core, typically using a bonding agent to ensure a strong and lasting bond. The final product undergoes quality control checks before being packaged and distributed. This precise manufacturing process ensures consistent quality and performance across different batches.
Lifespan and Maintenance Comparison Table
| Siding Material | Lifespan (Years) | Maintenance | Cost (Relative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulated Vinyl | 30-50 | Low | High |
| Traditional Vinyl | 20-30 | Low | Medium |
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Medium | High |
| Wood | 15-25 (with maintenance) | High | Medium |
Insulation Performance and Energy Savings

Insulated vinyl siding offers a significant advantage over traditional vinyl siding by incorporating an insulating layer, directly impacting a home’s energy efficiency and overall comfort. This integrated insulation dramatically reduces energy consumption, leading to substantial cost savings and a more comfortable living environment year-round. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Heat Transfer Reduction
The insulation layer in insulated vinyl siding acts as a barrier, significantly reducing the transfer of heat between the interior and exterior of your home. This is achieved through the insulation’s low thermal conductivity. Materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS) or polyisocyanurate (polyiso) are commonly used due to their excellent insulating properties. These materials trap air within their cellular structure, hindering the movement of heat molecules. In the summer, this prevents the external heat from easily penetrating your walls, keeping your home cooler. Conversely, in the winter, it minimizes heat loss from the interior, keeping your home warmer. The result is a more stable indoor temperature, reducing the strain on your HVAC system.
R-Value and its Impact
The R-value is a crucial metric indicating the insulating effectiveness of a material. A higher R-value signifies better insulation. Insulated vinyl siding typically offers an R-value ranging from R-5 to R-8, depending on the thickness and type of insulation used. This improved R-value translates directly to reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling. A home with higher R-value siding requires less energy to maintain a comfortable temperature, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. The enhanced thermal performance also contributes to improved comfort levels by minimizing temperature fluctuations throughout the day and night.
Factors Influencing Overall Energy Efficiency
While insulated vinyl siding contributes significantly to energy efficiency, it’s essential to consider other factors that influence a home’s overall thermal performance. These include the quality of windows and doors, the level of air sealing around the home, and the overall design and construction of the building envelope. Proper insulation in the attic, walls, and basement is also crucial. A comprehensive approach to energy efficiency involves optimizing all these elements to achieve maximum savings. Insulated vinyl siding acts as one important component within this larger strategy.
Case Studies and Energy Savings Demonstrations
Several studies have demonstrated the substantial energy savings achievable with insulated vinyl siding. For example, a study conducted by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory showed that homes retrofitted with insulated vinyl siding experienced an average reduction in energy consumption of 15-20% compared to homes with standard vinyl siding. Similarly, a homeowner in Minnesota reported a 12% decrease in their annual heating costs after installing insulated vinyl siding. These results highlight the significant potential for cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Comparative Energy Cost Savings
The following table illustrates the potential energy cost savings over a ten-year period for a typical home, comparing homes with and without insulated vinyl siding. These figures are estimates and can vary depending on factors such as climate, energy prices, and home size.
| Year | Home without Insulated Vinyl Siding (Annual Cost) | Home with Insulated Vinyl Siding (Annual Cost) | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 2 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 3 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 4 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 5 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 6 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 7 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 8 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 9 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| 10 | $2400 | $2040 | $360 |
| Total (10 years) | $24000 | $20400 | $3600 |
Installation and Application Methods

Installing insulated vinyl siding might seem daunting, but with the right approach and tools, it’s a manageable DIY project, or a straightforward job for experienced contractors. This section details the process, potential pitfalls, and best practices for a successful installation that maximizes the energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal of your home. Remember, proper installation is crucial for warranty validity and long-term performance.
Preparation and Surface Assessment
Before you even touch a single siding panel, thorough preparation is paramount. This involves a detailed inspection of the existing wall surface. Identify any damaged areas, such as rotting wood or loose sheathing, and repair them immediately. This might involve replacing damaged wood, patching holes, and ensuring a solid, level surface for the siding to adhere to. Furthermore, remove any existing siding, trim, or other obstructions. Clean the surface thoroughly, removing dirt, debris, and any loose paint. A properly prepared surface is the foundation of a successful siding installation. Failing to address these issues early on can lead to significant problems down the line, impacting both the aesthetics and the longevity of your new siding.
Installation Steps
The installation process typically begins with the installation of starter strips along the bottom of the wall. These provide a level base for the first row of siding panels. Next, install the first row of siding panels, ensuring proper alignment and overlap. Each subsequent row is then installed, overlapping the previous row according to the manufacturer’s instructions. J-channels and other trim pieces are installed around windows, doors, and corners to provide a clean and professional finish. Finally, install the final cap pieces to complete the installation.
- Step 1: Measure and cut starter strips to fit the length of each wall section. Secure them to the wall using appropriate fasteners.
- Step 2: Install the first row of siding panels, ensuring proper alignment and overlap. Use a level to maintain consistent spacing and prevent sagging.
- Step 3: Continue installing subsequent rows, overlapping each panel according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use a nail punch to set the fasteners below the surface of the siding.
- Step 4: Install J-channels and other trim pieces around windows, doors, and corners to create a professional finish. Ensure proper alignment and secure fastening.
- Step 5: Install the final cap pieces to complete the installation. Carefully cut and fit the pieces to ensure a snug and seamless finish.
Tools and Materials
Success hinges on having the right tools and materials. This includes a measuring tape, level, utility knife, hammer, nail gun (optional but recommended for efficiency), siding fasteners, starter strips, J-channels, and, of course, the insulated vinyl siding panels themselves. Using high-quality materials and appropriate tools ensures a professional finish and extends the lifespan of your siding. Investing in a good quality nail gun can significantly speed up the installation process, especially for larger projects. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for specific tool and material recommendations.
Addressing Installation Challenges
Uneven walls present a common challenge. Addressing this requires careful planning and potentially the use of shims to ensure the siding panels are installed straight and level. Another challenge can be working around existing features like windows and doors. Precise measurements and cuts are essential to achieve a clean and professional-looking finish in these areas. Finally, weather conditions can significantly impact the installation process. Avoid working in extreme heat or cold, and be mindful of wind and rain. Planning your project around favorable weather conditions will ensure a smoother and more efficient installation.
Different Installation Techniques
While the basic principles remain consistent, minor variations in technique can exist depending on the specific siding system and manufacturer’s recommendations. Some systems may utilize a different fastening method or require specialized tools. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for the most accurate and up-to-date installation guidelines. Ignoring these instructions can void warranties and lead to premature failure of the siding. The most critical aspect is to maintain consistency in spacing, alignment, and fastening throughout the installation process, regardless of the specific technique employed.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Insulated vinyl siding offers significant long-term benefits, but the initial investment requires careful consideration. Understanding the cost breakdown and potential return on investment (ROI) is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will analyze the various cost factors and project potential savings over time, helping you determine if this upgrade aligns with your financial goals.
Cost Breakdown of Insulated Vinyl Siding
The total cost of insulated vinyl siding installation is influenced by several key factors. Material costs vary depending on the chosen style, color, and manufacturer. Higher-end options with enhanced features, such as thicker insulation or more intricate designs, naturally command higher prices. Labor costs, representing a significant portion of the overall expense, are affected by the project’s complexity (e.g., intricate trim work, extensive repairs needed before installation), the size of the house, and regional labor rates. Permitting fees and any necessary repairs to the underlying structure also contribute to the final cost. For example, a 2,000 square foot home might see material costs ranging from $8,000 to $16,000, while labor could add another $6,000 to $12,000 or more, depending on location and project specifics.
Factors Influencing Overall Cost
Material selection significantly impacts the price. Premium brands offering superior durability and insulation properties typically cost more than standard options. The complexity of the house’s exterior also plays a crucial role. Homes with numerous architectural details, such as dormers or bay windows, require more intricate installation, leading to higher labor costs. Regional variations in labor rates and material availability further influence the overall expense. In areas with a high demand for skilled labor, installation costs will likely be higher. Finally, the condition of the existing siding impacts the project’s cost. If significant repairs or removal of old siding are needed, these added expenses must be factored into the total cost.
Comparing Initial Investment with Long-Term Savings
While the upfront investment in insulated vinyl siding can be substantial, the long-term energy savings and potential increase in home value often outweigh the initial expense. The enhanced insulation provided by the siding reduces energy consumption for heating and cooling, leading to lower utility bills. Furthermore, improved curb appeal resulting from a fresh, updated exterior can increase the home’s market value, adding to the overall return on investment. Consider a scenario where a homeowner invests $15,000 in insulated vinyl siding and experiences an annual energy savings of $500. Over 10 years, this translates to a $5,000 savings, significantly reducing the initial investment’s impact. An appraisal showing a $7,000 increase in home value further strengthens the financial case.
Return on Investment (ROI) for Insulated Vinyl Siding
Calculating the ROI for insulated vinyl siding involves comparing the total cost of the project to the accumulated savings from reduced energy bills and any increase in property value. The ROI can be expressed as a percentage, indicating the return on the initial investment over a specific period. Several factors affect the ROI calculation, including energy prices, climate conditions, the efficiency of the insulation, and the length of time the siding remains in place. For instance, a higher energy price environment leads to greater energy savings and thus, a better ROI. Conversely, in a mild climate, energy savings might be less substantial, affecting the ROI calculation. A detailed analysis, factoring in all these variables, is essential for an accurate assessment.
Potential Cost Savings Over Time
The following table illustrates potential cost savings over 10, 15, and 20 years, assuming an annual energy savings of $500 and no change in home value:
| Years | Annual Energy Savings | Cumulative Energy Savings | Potential ROI (excluding home value increase) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | $500 | $5,000 | 33% |
| 15 | $500 | $7,500 | 50% |
| 20 | $500 | $10,000 | 67% |
Aesthetic Considerations and Design Options
Insulated vinyl siding offers a remarkable blend of functionality and aesthetics, allowing homeowners to enhance their curb appeal while enjoying superior energy efficiency. The wide array of styles, colors, and textures available ensures that there’s a perfect option to complement any architectural style and personal preference. Choosing the right siding involves careful consideration of several key design elements to achieve a cohesive and visually appealing exterior.
Available Styles, Colors, and Textures
Insulated vinyl siding comes in a vast spectrum of styles, colors, and textures designed to mimic the look of more expensive materials like wood, brick, or stone, without the associated maintenance. The color palette ranges from classic neutrals to bold and vibrant hues, allowing for endless customization possibilities. Textures vary from smooth finishes to those that replicate the natural grain of wood or the ruggedness of stone, offering a level of realism that’s hard to match. For example, a homeowner aiming for a rustic charm might opt for a wood-grain texture in a warm brown tone, while someone seeking a modern aesthetic might prefer a clean, smooth white finish. Many manufacturers offer a wide variety of color options within each style and texture to cater to diverse tastes.
Insulated Vinyl Siding and Architectural Styles
The versatility of insulated vinyl siding makes it suitable for a wide range of architectural styles. For instance, a traditional colonial home might be beautifully complemented by siding that mimics clapboard or shingle patterns in muted earth tones. A contemporary home, on the other hand, might benefit from sleek, horizontal panels in a modern gray or charcoal. Ranch-style homes often look stunning with a combination of vertical and horizontal siding, adding visual interest and depth. The key is to select a style and color that harmonizes with the overall design of the house and its surroundings. Think of the subtle interplay of colors and textures – a craftsman style house might look great with a darker brown siding with contrasting trim, while a more minimalist home would benefit from a monochromatic palette.
Key Design Elements for Choosing Insulated Vinyl Siding
Several key design elements influence the overall aesthetic impact of insulated vinyl siding. These include the siding profile (e.g., clapboard, shake, panel), color selection, trim details, and the integration of other exterior elements such as windows, doors, and landscaping. Consider the existing architectural style of your home, the surrounding landscape, and your personal preferences when making these choices. For example, a large home might benefit from a bolder color choice, while a smaller home might look better with a more subdued palette. The use of contrasting trim colors can add visual interest and highlight architectural details.
Enhancing Aesthetic Appeal with Siding Profiles and Accessories
Different siding profiles and accessories can significantly impact the overall aesthetic appeal. For instance, using a combination of vertical and horizontal siding can create visual depth and texture. Adding decorative trim, such as corner boards, window surrounds, and fascia, enhances the architectural details and adds a touch of elegance. Accessories like shutters, which can be chosen to match or contrast with the siding color, add further visual interest and personality. Consider the scale of your home; larger homes might accommodate more elaborate trim details, while smaller homes might benefit from simpler designs. The choice of accessories can transform the look from plain to stunning.
Visual Guide: Design Options and Applications
- Classic Clapboard: A timeless and versatile choice, ideal for traditional homes. Imagine a two-story colonial house clad in creamy white clapboard siding, accented by dark green shutters and white trim. This creates a classic, elegant look.
- Modern Panel: Clean lines and a contemporary feel, perfect for modern and minimalist homes. Picture a sleek, low-profile home with large windows, covered in smooth gray panel siding, showcasing a minimalist, modern aesthetic.
- Rustic Shake: Adds texture and warmth, ideal for homes with a rustic or craftsman style. Envision a charming cabin-style home with brown shake-style siding, complementing the natural surroundings and evoking a cozy, rustic feel.
- Stone-look Siding: Mimics the look of natural stone, creating a luxurious and durable exterior. Imagine a stately home with large stone-look vinyl siding, adding an element of grandeur and sophistication to the façade.
Ultimately, insulated vinyl siding presents a smart investment for homeowners seeking a beautiful, energy-efficient, and low-maintenance exterior solution. By understanding its composition, installation process, and long-term benefits, you can confidently choose a siding option that enhances your home’s curb appeal while boosting its energy efficiency and increasing its overall value. Weigh the pros and cons carefully, considering your budget and aesthetic preferences to make the best choice for your property.
Questions Often Asked
Is insulated vinyl siding recyclable?
While not all vinyl is readily recyclable, some manufacturers offer recycling programs or partnerships with recycling facilities. Check with your supplier or local recycling center for options.
How does insulated vinyl siding affect home insurance premiums?
Energy-efficient upgrades like insulated vinyl siding can sometimes lead to lower home insurance premiums. Contact your insurance provider to inquire about potential discounts.
Can insulated vinyl siding be installed over existing siding?
In some cases, yes. However, it depends on the condition of the existing siding and the type of underlying structure. A professional assessment is crucial before undertaking such a project to ensure proper installation and avoid potential issues.
What are the warranty options for insulated vinyl siding?
Warranty terms vary depending on the manufacturer and specific product. Look for warranties covering material defects, labor, and color fading to protect your investment.
Does insulated vinyl siding require special cleaning?
Regular cleaning with water and a soft brush is usually sufficient. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that can damage the surface.



