Transforming your mobile home’s exterior? Choosing the right siding isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s a strategic investment impacting curb appeal, energy efficiency, and long-term value. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of mobile home siding, exploring various materials, installation techniques, maintenance strategies, and cost considerations to help you make an informed decision that perfectly complements your lifestyle and budget.
From understanding the nuances of vinyl, aluminum, fiber cement, and wood siding to mastering DIY repairs and maximizing your home’s energy efficiency, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll also explore the latest design trends and help you calculate the total cost of your project, ensuring you get the best bang for your buck. Get ready to unlock the full potential of your mobile home’s exterior.
Types of Mobile Home Siding

Choosing the right siding for your mobile home is a crucial decision impacting both aesthetics and longevity. The material you select will significantly influence your home’s curb appeal, its resistance to the elements, and the overall maintenance required. Let’s delve into the most common options available.
Vinyl Siding
Vinyl siding remains a popular choice for mobile homes due to its affordability and low maintenance. It’s available in a wide array of colors and styles, mimicking the look of wood or brick. However, it’s susceptible to damage from impact and extreme temperatures, potentially leading to cracking or warping. Its lifespan is generally shorter compared to other options, and it doesn’t offer significant insulation value. While it’s easy to clean, significant damage often necessitates panel replacement.
Aluminum Siding
Aluminum siding offers superior durability and resistance to fire and insects compared to vinyl. It’s lightweight, making installation relatively easy. Its reflective properties can help reduce energy costs by reflecting sunlight. However, aluminum can dent easily, and its metallic appearance might not appeal to everyone. While it requires minimal maintenance, scratches and dents are noticeable and can affect the aesthetic appeal over time. It also lacks significant insulation properties.
Fiber Cement Siding
Fiber cement siding is a high-performance option, boasting exceptional durability and resistance to fire, rot, and insects. It offers superior insulation compared to vinyl and aluminum, contributing to lower energy bills. Its realistic wood-grain texture enhances aesthetic appeal, making it a premium choice. However, fiber cement siding is more expensive than vinyl or aluminum and is heavier, requiring more robust installation techniques. Maintenance involves regular cleaning to prevent staining.
Wood Siding
Wood siding provides a classic, natural look that many homeowners find appealing. It can be customized with various stains and finishes to match personal preferences. However, wood is susceptible to rot, insect infestation, and requires significant maintenance, including regular painting or staining and occasional repairs. It also offers less protection against fire compared to other options. The lifespan is heavily dependent on proper maintenance and climate conditions.
| Siding Type | Lifespan (Years) | Average Cost (per sq ft) | Insulation R-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 20-30 | $2-$5 | 0.05-0.1 |
| Aluminum | 40-50 | $3-$7 | 0.1-0.2 |
| Fiber Cement | 50-80 | $6-$12 | 0.2-0.5 |
| Wood | 20-40 (with maintenance) | $5-$15 | 0.1-0.3 |
Mobile Home Siding Installation

Installing new siding on your mobile home can significantly enhance its curb appeal and protect it from the elements. A successful installation requires careful planning, preparation, and execution. This guide provides a step-by-step process for installing vinyl siding, a popular and relatively easy-to-install option. Remember, safety is paramount throughout the entire project.
Exterior Preparation
Before installing any siding, thoroughly inspect your mobile home’s exterior. Address any existing damage, such as rotted wood, loose trim, or damaged sheathing. Repair or replace any compromised areas using appropriate materials. Clean the surface of the exterior walls, removing dirt, loose paint, and any other debris. This ensures proper adhesion and a smooth installation process. A pressure washer can be highly effective for this task, but always exercise caution to avoid damaging the underlying structure. Ensure the existing surface is completely dry before beginning the siding installation.
Tool and Material Checklist
Proper tools are essential for a smooth and efficient installation. You’ll need a measuring tape, level, utility knife, circular saw (with a fine-tooth blade for cutting vinyl siding), hammer, nail gun (optional, but highly recommended for speed and efficiency), caulk gun, and safety glasses. In addition to the siding itself, you’ll need J-channel, starter strip, corner trim, and flashing. Appropriate fasteners are also critical; use galvanized nails or screws designed for exterior use to prevent rust and corrosion. Remember to acquire enough materials to complete the entire project, accounting for waste and potential errors.
Vinyl Siding Installation Process
Begin by installing the starter strip along the bottom edge of the wall, ensuring it’s perfectly level. This provides a consistent base for the first row of siding. Next, install the J-channel around windows and doors, providing a neat finish and protecting the edges from the elements. Install corner trim pieces at exterior corners for a clean, professional look. Then, begin installing the siding panels, working from bottom to top and overlapping each panel according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use a level to ensure each panel is properly aligned. Fasten the panels securely, ensuring the nails are driven straight and don’t penetrate the siding too deeply. Remember to cut panels to size as needed using a sharp utility knife or circular saw, paying close attention to maintaining straight cuts and consistent panel lengths.
Cutting and Fitting Siding Panels
Accurate cutting is crucial for a professional-looking installation. Measure carefully before making any cuts. Use a sharp utility knife or circular saw with a fine-tooth blade for clean, precise cuts. For intricate cuts around windows or doors, use a jigsaw. Always allow for expansion and contraction of the vinyl siding, leaving a small gap between panels and trim. This prevents buckling or warping during temperature fluctuations.
Flashing and Crucial Components
Proper flashing is essential to prevent water intrusion. Install flashing above windows and doors, overlapping it with the siding to create a waterproof barrier. Flashing should extend beyond the width of the siding and be properly sealed with caulk. Similarly, ensure that all seams and joints are adequately caulked to prevent water leakage. A visual representation would show the starter strip at the bottom, followed by rows of overlapping siding panels. J-channel would be visible around windows and doors, with corner trim neatly finishing the exterior corners. Flashing would be clearly visible above windows and doors, extending under the siding and sealed with caulk. This comprehensive approach ensures a weathertight and aesthetically pleasing installation.
Mobile Home Siding Repair and Maintenance
Maintaining your mobile home’s siding is crucial for preserving its value and curb appeal. Neglecting repairs can lead to significant damage, impacting both aesthetics and the structural integrity of your home. Regular maintenance, however, can extend the lifespan of your siding considerably, saving you money on costly replacements down the line. This section details common problems, repair techniques, and preventative measures to keep your mobile home looking its best.
Common Mobile Home Siding Issues
Mobile home siding, particularly vinyl, is susceptible to several types of damage. Cracking is a frequent problem, often caused by impacts, temperature fluctuations, or settling of the home’s foundation. Exposure to the elements leads to fading, particularly in areas with intense sunlight. Severe weather events, such as hailstorms or strong winds, can cause more extensive damage, including dents, punctures, and even complete panel loss. Ignoring these issues can lead to further deterioration, potentially requiring more extensive and costly repairs. For instance, a small crack left unaddressed can expand, allowing moisture to penetrate and cause rot in the underlying structure.
Repairing Minor Vinyl Siding Damage
Minor repairs to vinyl siding are often manageable with basic tools and materials. Patching small holes involves cleaning the area, applying a compatible patching compound, and carefully smoothing it to match the surrounding siding. For larger holes or severely damaged panels, replacement is necessary. This involves carefully removing the damaged panel, measuring for a replacement, and securing the new panel using appropriate fasteners. Remember to use sealant around the edges of the replacement panel to prevent moisture intrusion. A simple example would be patching a small hole created by a stray ball; cleaning the area, applying a vinyl patching compound, and then painting to match the existing color would suffice. Replacing a hail-damaged panel would involve removing the damaged section, measuring the dimensions, purchasing a replacement, and securely attaching it with appropriate screws or nails, sealing around the edges.
Preventative Maintenance for Mobile Home Siding
Regular preventative maintenance is key to extending the life of your mobile home’s siding. Regular cleaning, ideally twice a year, using a mild detergent and soft brush, removes dirt, grime, and mildew, preventing damage and preserving the siding’s color. Annual inspections are also crucial. Look for cracks, holes, loose panels, or signs of fading. Addressing minor issues promptly prevents them from escalating into larger, more costly problems. For example, a homeowner who regularly inspects their siding might notice a small crack early on, allowing for a simple patch repair, rather than needing to replace an entire panel later due to water damage.
Tools and Materials for Mobile Home Siding Repairs
Having the right tools and materials on hand simplifies repairs and ensures a professional finish.
- Putty knife
- Caulk gun
- Measuring tape
- Utility knife
- Screwdriver (Phillips and flathead)
- Hammer
- Safety glasses
- Work gloves
- Vinyl siding patching compound
- Vinyl siding sealant
- Replacement siding panels (if needed)
- Paints or primers (to match existing siding)
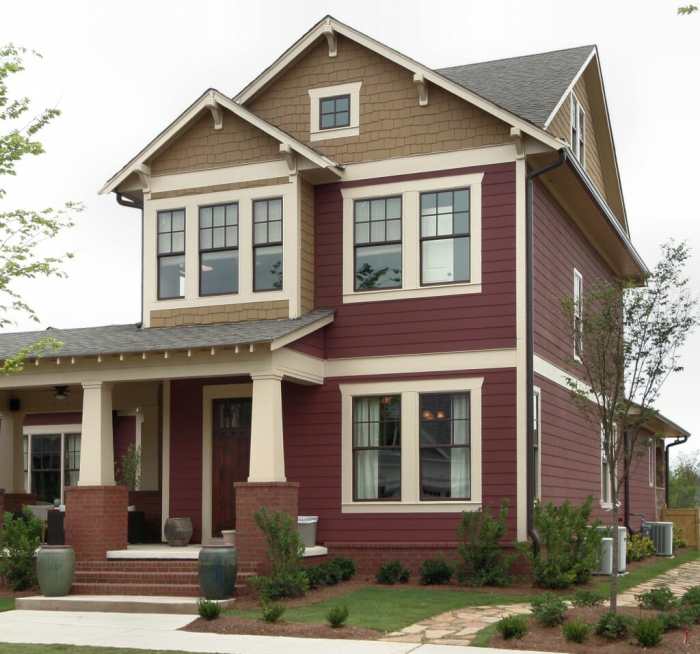
Siding Styles and Aesthetics

Choosing the right siding for your mobile home isn’t just about protection; it’s a powerful tool to dramatically enhance its curb appeal and overall value. The style, color, and texture you select significantly impact the home’s visual character, transforming it from ordinary to extraordinary. Let’s explore how different siding options can achieve this.
The variety of siding styles available allows for considerable personalization. Understanding these options and their impact on your home’s aesthetics is key to making an informed decision. From classic to contemporary, the possibilities are vast, allowing you to tailor your mobile home’s exterior to perfectly reflect your personal style and preferences.
Horizontal Siding Styles
Horizontal siding, a classic and widely popular choice, offers a clean, streamlined look. This style is often seen in traditional and ranch-style homes, lending a sense of simplicity and elegance. The horizontal lines can visually widen a home, making it appear more spacious. Variations include board and batten, where wider planks are paired with narrower strips, creating a more textured appearance. Another variation is shiplap, known for its clean lines and slightly overlapping planks. The choice of material, such as vinyl, wood, or metal, further impacts the overall aesthetic. For example, vinyl offers a low-maintenance, cost-effective option in a variety of colors, while wood provides a more rustic and natural feel.
Vertical Siding Styles
Vertical siding, in contrast to horizontal, creates a sense of height and sophistication. It can make a mobile home appear taller and more slender, an advantage for homes with lower profiles. This style is frequently used in contemporary and modern designs, lending a clean and minimalist feel. Vertical siding, much like horizontal, comes in various materials, including vinyl, fiber cement, and metal. The choice of material significantly influences the texture and overall aesthetic; for instance, metal siding provides a sleek, modern look, while fiber cement offers a more durable and sophisticated appearance.
Shake Siding Styles
Shake siding, mimicking the look of natural wood shakes, offers a rustic and charming aesthetic. This style often creates a cozy and inviting feel, especially suitable for homes with a more traditional or country-style design. The uneven texture and varied lengths of the “shakes” add visual interest and depth. While traditionally made from wood, modern shake siding often utilizes vinyl or fiber cement for low-maintenance benefits and durability. This imitation maintains the visual appeal of natural wood without the associated upkeep.
The Impact of Color and Texture
Color and texture play a crucial role in shaping the overall impression of your mobile home’s siding. Lighter colors, such as creams, whites, and pastels, can make a home appear larger and brighter, while darker colors, like grays, browns, and blues, can create a more dramatic and sophisticated look. The texture of the siding also contributes significantly to the aesthetic. Smooth siding offers a modern and clean appearance, while textured siding adds depth and visual interest. For instance, a rough-hewn texture might complement a rustic design, while a smooth, sleek finish would suit a modern style.
Enhancing Curb Appeal Through Siding
Strategic use of siding can significantly enhance a mobile home’s curb appeal. Using contrasting colors or textures on different sections of the home can add visual interest and create a focal point. For example, using darker siding around the base of the home can create a sense of grounding, while lighter siding on the upper portion can make it appear more spacious. Adding accents, such as decorative trim or shutters, can further elevate the overall design and create a more polished look. A well-planned siding scheme can transform a plain mobile home into a visually appealing and attractive property.
Design Considerations for Mobile Home Siding
Choosing the right siding requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure it complements your home’s architectural style and your personal preferences.
- Architectural Style: Consider the overall style of your mobile home. A modern home might benefit from sleek, vertical siding, while a traditional home might look better with horizontal siding or a shake style.
- Climate: Choose a siding material that is suitable for your local climate. For example, in areas with extreme temperatures, you might want to consider a material that is resistant to expansion and contraction.
- Maintenance: Consider the level of maintenance you are willing to undertake. Some siding materials, such as vinyl, are low-maintenance, while others, such as wood, require more regular upkeep.
- Budget: Siding materials vary significantly in cost. Consider your budget when making your selection.
- Color and Texture: Choose colors and textures that complement your home’s overall aesthetic and the surrounding landscape.
- Durability: Select a durable material that can withstand the elements and last for many years.
Cost Considerations for Mobile Home Siding
Replacing your mobile home’s siding is a significant investment, impacting both aesthetics and property value. Understanding the cost factors upfront is crucial for budgeting and avoiding unpleasant surprises. This section breaks down the key cost components, helping you make informed decisions.
Material Costs
Material costs represent a substantial portion of your overall siding project expense. The type of siding you choose dramatically affects this figure. Vinyl siding, for instance, is generally the most budget-friendly option, while more durable materials like aluminum or fiber cement command higher prices. Consider the square footage of your mobile home’s exterior walls and the cost per square foot for your chosen siding material. Don’t forget to factor in additional materials like trim, flashing, and fasteners, which can easily add 10-20% to your initial material estimate. For example, a 1,000 square foot mobile home might require 1,200 square feet of siding to account for waste and cuts. Pricing will vary greatly depending on the manufacturer and retailer. Always get multiple quotes to ensure you are receiving competitive pricing.
Labor Costs
Labor costs are equally important and often overlooked. The complexity of the job, the size of your mobile home, and the contractor’s experience all influence labor expenses. A simple siding replacement on a smaller mobile home might cost less than a more complex project involving extensive repairs or unusual architectural features. Expect to pay hourly rates, which can vary depending on your location and the contractor’s reputation. It’s essential to obtain detailed quotes from multiple contractors that clearly Artikel labor costs, including any potential extra charges for unforeseen issues. Remember that experienced contractors often charge more but may complete the job faster and more efficiently, potentially saving you money in the long run.
Permits and Inspections
Depending on your local regulations, you might need permits for your siding replacement project. Permit fees can range widely depending on your location and the scope of the work. It’s essential to check with your local building department early in the planning process to determine permit requirements and associated costs. Inspections are also common, and failure to obtain necessary permits or pass inspections could result in delays and additional expenses. Budgeting for these unforeseen costs is crucial to avoid project delays and potential fines.
Cost Comparison of Siding Materials
Different siding materials offer varying levels of durability, maintenance requirements, and initial costs. Vinyl siding is typically the least expensive upfront but might require more frequent repairs over its lifespan. Aluminum siding offers excellent durability and longevity, although the initial cost is higher. Fiber cement siding is a premium option, known for its exceptional durability and fire resistance, but comes with the highest initial cost. To compare cost-effectiveness, consider the total cost of ownership over the siding’s lifespan, including initial purchase, installation, maintenance, and potential repairs. For example, while vinyl might be cheaper initially, frequent repairs over 15 years could make its total cost exceed that of aluminum siding over the same period. A thorough cost-benefit analysis considering the expected lifespan of each material is vital.
Cost Breakdown and Estimation Guide
To estimate the total cost, consider this simplified breakdown:
| Cost Category | Estimated Percentage of Total Cost |
|---|---|
| Material Costs (Siding, Trim, Fasteners) | 40-50% |
| Labor Costs (Installation, Waste Removal) | 40-50% |
| Permits and Inspections | 5-10% |
| Contingency (Unforeseen Expenses) | 5-10% |
To create a personalized estimate:
1. Measure your mobile home’s exterior: Calculate the total square footage of the siding to be replaced.
2. Obtain material quotes: Get quotes from multiple suppliers for your chosen siding material, including trim and fasteners.
3. Get labor quotes: Obtain detailed quotes from at least three contractors, specifying the scope of work.
4. Inquire about permits and inspections: Contact your local building department to determine permit requirements and fees.
5. Add a contingency: Include a buffer (5-10%) to cover unforeseen expenses.
By following these steps and using the percentage breakdown above, you can develop a reasonable estimate for your mobile home siding replacement project. Remember that this is just a guide, and actual costs may vary.
Environmental Impact of Mobile Home Siding
Choosing siding for your mobile home involves more than just aesthetics and cost; it significantly impacts the environment. From manufacturing to disposal, the materials used have a considerable carbon footprint and influence long-term sustainability. Understanding these environmental implications is crucial for making informed decisions that align with eco-conscious living.
Production and Disposal of Mobile Home Siding Materials
The manufacturing process of different siding materials varies greatly, influencing their environmental impact. Vinyl siding, for example, is derived from petroleum, a non-renewable resource. Its production requires significant energy, releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Conversely, aluminum siding, while recyclable, also demands considerable energy for its initial production. Wood siding, a more renewable option, has its own set of environmental considerations depending on its sourcing and treatment; sustainably harvested wood with minimal chemical treatments has a smaller footprint. Finally, fiber cement siding, a composite material, requires energy for its production and contains cement, which has its own environmental impact. Disposal presents further challenges. Vinyl siding is not readily biodegradable and often ends up in landfills. Aluminum and some wood siding are recyclable, reducing landfill waste, while fiber cement siding requires careful handling during disposal.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties of Siding Materials
The energy efficiency of mobile home siding directly affects energy consumption and, consequently, the carbon footprint of the dwelling. Materials with superior insulation properties reduce the need for heating and cooling, minimizing energy usage and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, vinyl siding, while not inherently insulating, can be installed over appropriate insulation to improve energy efficiency. However, some studies have shown that lighter colored siding can reflect more sunlight and reduce cooling costs, offering a passive approach to energy conservation. Conversely, dark-colored siding tends to absorb more heat, increasing energy demands for cooling. Fiber cement siding, with its density, often provides better insulation than vinyl, contributing to lower energy consumption. The overall thermal performance depends not only on the siding material itself but also on the underlying insulation and the overall building envelope.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Siding Options
Several sustainable and eco-friendly options are available for mobile home siding, offering environmentally conscious alternatives to traditional materials. Recycled materials, such as recycled plastic or aluminum siding, can significantly reduce the environmental burden compared to virgin materials. Choosing siding made from rapidly renewable resources, like bamboo, offers another pathway to sustainability. Furthermore, opting for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints reduces the release of harmful chemicals into the atmosphere during and after application. Low-VOC paints minimize indoor air pollution and contribute to a healthier environment. Careful consideration of the entire lifecycle—from material sourcing to disposal—is key to selecting truly sustainable siding.
Environmental Footprint Comparison of Siding Materials
| Siding Material | Production Energy Consumption | Recyclability | Insulation Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | High (petroleum-based) | Low | Moderate (dependent on installation) |
| Aluminum | High (energy-intensive production) | High | Low |
| Wood | Variable (dependent on sourcing and treatment) | Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Fiber Cement | Moderate | Low | High |
Ultimately, selecting the right mobile home siding is a balancing act between aesthetics, durability, cost, and environmental impact. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of each material, understanding the installation process, and implementing a proactive maintenance plan, you can ensure your siding enhances your home’s value and beauty for years to come. Remember, a well-chosen siding isn’t just a cosmetic upgrade; it’s a strategic investment in your home’s longevity and your peace of mind. Now go transform that curb appeal!
FAQ Compilation
Can I install mobile home siding myself?
While DIY is possible for some types of siding, particularly vinyl, it’s often a complex project requiring specialized tools and skills. Improper installation can lead to leaks and damage, potentially voiding warranties. Consider the scope of the project and your skill level before attempting a DIY installation. Professional installation ensures a long-lasting, weather-tight result.
How often should I clean my mobile home siding?
Regular cleaning, at least once or twice a year, is crucial for maintaining your siding’s appearance and longevity. Use a soft brush, mild detergent, and a garden hose to remove dirt, grime, and debris. Avoid harsh chemicals or pressure washers, which can damage the siding.
What’s the warranty on mobile home siding?
Warranties vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and type of siding. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for details on coverage and limitations. Proper installation is often a condition of the warranty.
How long does mobile home siding typically last?
The lifespan of mobile home siding depends on the material, climate, and maintenance. Vinyl siding can last 20-30 years, aluminum 40-50 years, and fiber cement even longer. Proper maintenance significantly extends the lifespan of any siding material.
What are some common signs of siding damage?
Look for cracks, holes, fading, discoloration, loose or damaged panels, and signs of water damage. Address minor damage promptly to prevent further deterioration and costly repairs.