Thinking about siding your house? The cost can vary wildly, making it crucial to understand the factors involved before you even pick up a paintbrush. From material selection—vinyl, wood, fiber cement, metal—to labor costs that fluctuate regionally, this guide dives deep into the average cost of siding a house, helping you navigate the complexities and make informed decisions. We’ll break down everything from initial estimates to long-term maintenance, empowering you to budget effectively and achieve your dream home exterior.
This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the trade-offs. A cheaper upfront cost might translate to higher maintenance expenses down the line. We’ll explore the lifespan of different siding materials, helping you weigh the short-term investment against long-term value. We’ll also cover regional variations in labor and material costs, ensuring you’re prepared for whatever your local market throws at you. By the end, you’ll be equipped to confidently approach your siding project with a realistic budget and clear understanding of what to expect.
Factors Influencing Siding Costs
The cost of siding your house isn’t a one-size-fits-all figure. Several key factors significantly impact the final price, from the type of material you choose to the complexity of your home’s design and your geographic location. Understanding these variables is crucial for accurate budgeting and avoiding unpleasant surprises during your home improvement project. This analysis will break down the major cost drivers, empowering you to make informed decisions.
Siding Material Costs
The type of siding you select dramatically affects the overall expense. Different materials offer varying degrees of durability, aesthetics, and maintenance requirements, all influencing their price point. Vinyl siding, for example, is generally the most budget-friendly option, while wood siding, especially premium varieties, commands a higher price. Fiber cement provides a durable, low-maintenance alternative, falling somewhere in between. Below is a comparative table illustrating typical cost ranges per square foot:
| Siding Material | Cost per Square Foot (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $3 – $8 | Wide range reflects quality and style variations. |
| Wood | $8 – $20+ | Price depends heavily on wood type (e.g., cedar, redwood) and grade. |
| Fiber Cement | $6 – $15 | Cost varies based on thickness and texture. |
| Metal | $7 – $20+ | Aluminum is generally less expensive than steel or zinc. |
House Size and Complexity
The square footage of your home is a direct determinant of siding costs. Larger homes naturally require more material and labor, leading to higher overall expenses. Beyond size, the complexity of your home’s architecture plays a significant role. Features such as dormers, multiple stories, intricate trim work, and numerous angles increase labor time and material waste, thereby escalating the cost. For instance, a two-story colonial with dormers and elaborate trim will cost considerably more to side than a single-story ranch.
Regional Variations in Labor and Materials
Labor costs fluctuate significantly across different regions of the country. Areas with high costs of living or strong union presence tend to have higher labor rates for siding installation. Similarly, material availability and transportation costs can influence pricing. Siding materials might be more expensive in regions with limited local suppliers or where transportation distances are substantial. For example, a project in a remote area may have significantly higher transportation costs compared to an urban setting.
Permit Fees and Other Expenses
Obtaining necessary permits from your local building department is a mandatory step before starting any siding project. Permit fees vary depending on your location and the scope of the project. Additionally, consider other associated costs such as demolition of old siding, preparation of the underlying structure, and potential repairs or upgrades required before siding installation. These hidden costs can sometimes add up significantly.
Types of Siding and Their Costs

Choosing the right siding for your home is a crucial decision impacting both aesthetics and long-term budget. Understanding the cost variations between different materials is essential for making an informed choice. This section breaks down the price points and associated benefits and drawbacks of popular siding options, helping you navigate this important home improvement project.
Vinyl Siding Costs and Considerations
Vinyl siding remains a popular choice due to its affordability and low maintenance. It’s typically the least expensive option, making it attractive for budget-conscious homeowners. However, its durability and aesthetic appeal might not match higher-end materials. The initial cost savings can be offset by a shorter lifespan compared to other options, potentially leading to earlier replacement costs.
- Cost Range: $3-$12 per square foot, depending on quality, style, and installation.
- Pros: Low initial cost, low maintenance, wide variety of colors and styles, easy installation.
- Cons: Can be easily damaged, susceptible to fading, limited lifespan (15-30 years), less energy-efficient than some alternatives.
- Lifespan and Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning is usually sufficient. However, damage repair can be costly.
Wood Siding Costs and Considerations
Wood siding offers a classic, natural look that many homeowners find appealing. However, it comes with a higher price tag and significantly more maintenance requirements than vinyl. The cost varies drastically depending on the wood type (e.g., cedar, redwood) and the quality of the finish. Higher-end woods require more frequent maintenance to prevent rot and insect damage.
- Cost Range: $7-$25+ per square foot, depending on wood type, finish, and installation.
- Pros: Natural beauty, high durability (with proper maintenance), can increase home value.
- Cons: High initial cost, requires significant maintenance (painting, sealing, repairs), susceptible to rot, insects, and fire damage.
- Lifespan and Maintenance: With proper maintenance, wood siding can last 50 years or more. However, regular painting, sealing, and repairs are necessary to extend its lifespan and prevent damage.
Fiber Cement Siding Costs and Considerations
Fiber cement siding offers a good balance between cost, durability, and aesthetics. It mimics the look of wood but is more resistant to damage from moisture, insects, and fire. This translates to lower long-term maintenance costs. However, its installation is more complex than vinyl, impacting the overall cost.
- Cost Range: $8-$15+ per square foot, depending on style, texture, and installation.
- Pros: Durable, fire-resistant, low maintenance, resists rot and insects, excellent lifespan.
- Cons: Higher initial cost than vinyl, more difficult to install than vinyl, can be brittle and prone to cracking if mishandled.
- Lifespan and Maintenance: Can last 50 years or more with minimal maintenance, usually just occasional cleaning.
Metal Siding Costs and Considerations
Metal siding, often made of aluminum or steel, is exceptionally durable and long-lasting. It’s highly resistant to fire, insects, and rot, requiring minimal maintenance. While the initial cost is relatively high, the extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs can result in long-term cost savings. The modern aesthetic appeal is another significant advantage.
- Cost Range: $9-$20+ per square foot, depending on metal type, finish, and installation.
- Pros: Extremely durable, fire-resistant, low maintenance, long lifespan (50+ years), various colors and styles.
- Cons: High initial cost, can dent or scratch, may require professional installation.
- Lifespan and Maintenance: Metal siding boasts an exceptionally long lifespan with minimal maintenance; occasional cleaning is usually sufficient.
Labor Costs and Installation Process

Understanding labor costs is crucial for accurately budgeting your siding project. Labor represents a significant portion of the overall expense, often rivaling or exceeding the cost of the siding materials themselves. Factors like the installer’s skill, project complexity, and location all play a vital role in determining the final price. Let’s break down the process and the associated costs.
Professional siding installation is a multi-step process requiring precision and expertise. A rushed or poorly executed job can lead to costly repairs down the line, compromising both the aesthetic appeal and the structural integrity of your home. Therefore, choosing a qualified and experienced contractor is paramount.
Siding Installation Steps
The typical siding installation process involves several key stages, each contributing to the overall labor costs. A well-defined sequence ensures a smooth, efficient, and high-quality outcome. Consider these steps as a benchmark, though specific tasks might vary depending on the type of siding and the condition of your home.
- Preparation: This initial phase involves meticulous measurements, removal of old siding (if necessary), and surface preparation. This includes addressing any underlying issues such as rotted wood or damaged sheathing. Thorough preparation is essential for a successful installation and prevents future problems.
- Installation of Underlayment (if needed): Depending on the type of siding and existing wall conditions, an underlayment might be necessary. This provides an extra layer of protection against moisture and improves insulation. The installation of this layer is crucial for longevity and performance.
- Siding Installation: This is the core of the process, involving the careful and precise placement of each siding panel, ensuring proper alignment, overlap, and fastening. This stage demands expertise to achieve a seamless, visually appealing finish.
- Trim and Finishing: This includes installing trim pieces around windows, doors, and corners. This stage requires attention to detail and precise cuts to maintain a clean and professional appearance. It’s the final touch that makes all the difference.
- Cleanup: After installation, a thorough cleanup is necessary to remove debris and restore the surrounding area to its pre-installation condition. This includes disposing of waste materials responsibly.
Factors Influencing Labor Costs
Several factors significantly impact the labor costs associated with siding installation. Understanding these factors allows for more accurate budgeting and informed decision-making.
The experience and reputation of the installer directly correlate with labor costs. Highly skilled and experienced installers command higher rates due to their expertise and efficiency. A less experienced installer might offer lower rates, but this could potentially lead to lower quality work or increased project timelines.
Project complexity greatly influences labor costs. Homes with intricate architectural details, multiple angles, or significant repairs require more time and effort, leading to higher labor expenses. A simple, rectangular home will generally require less labor than a Victorian-style house with numerous gables and dormers.
Geographical location also plays a role. Labor costs vary across regions due to differences in the cost of living, market demand, and prevailing wage rates. Installation in a high-cost-of-living area will naturally result in higher labor charges compared to a more rural location.
Scope of Work and Labor Costs
The scope of work, particularly the removal of existing siding, significantly impacts labor costs. Removing old siding adds considerable time and effort to the project. The condition of the existing siding further complicates matters; severely damaged or deteriorated siding requires more extensive removal and preparation, increasing the overall labor expense. For instance, removing asbestos siding requires specialized handling and disposal procedures, adding substantial costs. Conversely, if the existing siding is in good condition and can be left in place, the overall labor costs will be lower.
Estimating and Budgeting for Siding Projects
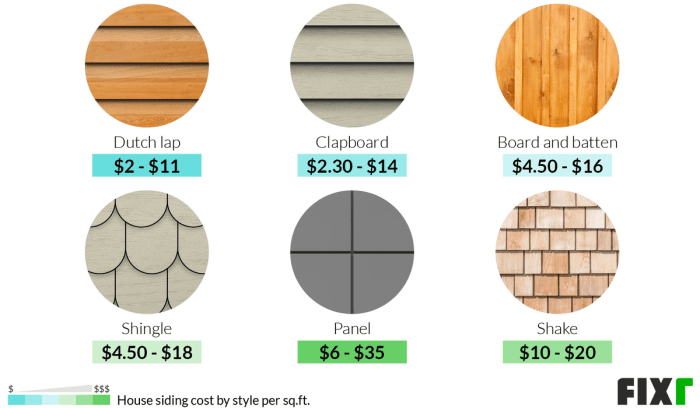
Accurately estimating the cost of your siding project is crucial to avoid unexpected expenses and ensure a smooth renovation process. A well-defined budget, factoring in all potential costs, will prevent financial surprises and allow for informed decision-making throughout the project. This section provides a practical guide to help you navigate the budgeting process effectively.
Step-by-Step Cost Estimation Guide
Accurate cost estimation requires a methodical approach. Begin by gathering necessary information and then systematically calculating the various cost components. Ignoring even seemingly small details can lead to significant budget overruns.
- Measure Your House: Precisely measure the total surface area of your house that requires siding. This includes walls, gables, and any other areas needing replacement. Account for windows and doors by subtracting their areas from the total. Consider using professional measuring services for complex house shapes to ensure accuracy.
- Choose Your Siding Material: Research different siding materials (vinyl, fiber cement, wood, etc.) and select the one that aligns with your budget and aesthetic preferences. Obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers to compare prices.
- Calculate Material Costs: Once you’ve chosen your siding, multiply the total surface area by the cost per square foot of the chosen material, including necessary extras like trim and flashing. Don’t forget to factor in waste – typically 5-10% extra material is recommended.
- Determine Labor Costs: Contact several siding contractors and request detailed quotes. These quotes should clearly specify the labor costs, including preparation, installation, and cleanup. Compare quotes to find competitive pricing and ensure you understand the scope of work included.
- Factor in Permits and Other Fees: Obtain necessary permits from your local authorities and factor their cost into your budget. Also include costs for waste disposal, potential repairs to underlying structures, and any other associated fees.
- Include Contingency Costs: Always add a contingency buffer of 10-15% to your total estimated cost. This accounts for unforeseen expenses, material price fluctuations, or unexpected complications during installation.
Sample Siding Project Budget
This table provides a sample budget. Your actual costs will vary based on your location, house size, siding material choice, and contractor selection.
| Cost Item | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Materials (Siding, Trim, Flashing) | $8,000 |
| Labor (Installation, Preparation, Cleanup) | $6,000 |
| Permits and Fees | $500 |
| Contingency (15%) | $2,100 |
| Total Estimated Cost | $16,600 |
Cost-Effective Siding Strategies
Finding cost-effective siding options doesn’t necessarily mean compromising on quality. Strategic planning can significantly impact your overall cost without sacrificing durability or aesthetics.
- Consider less expensive siding materials: Vinyl siding often offers a good balance of affordability and durability. While not as long-lasting as fiber cement, it’s significantly cheaper.
- Shop around for materials and labor: Obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers and contractors to compare prices and find the best deals. Negotiate prices where possible.
- DIY where feasible: If you have experience with home improvement projects, consider undertaking some aspects of the installation yourself, such as preparation work. However, for complex installations, professional help is advisable.
- Time your project strategically: Contractors often offer discounts during the off-season. Scheduling your project during these periods can result in cost savings.
Utilizing Online Cost Estimation Tools
Many online calculators and tools provide preliminary cost estimates for siding projects. These tools often require inputting basic information such as house size, siding type, and location. While these estimates aren’t perfectly precise, they offer a valuable starting point for budgeting and comparison. Remember to use several tools and compare results before finalizing your budget. Always consult with a contractor for a detailed and accurate quote.
Visual Examples of Different Siding Styles
Choosing the right siding dramatically impacts your home’s curb appeal and overall value. Understanding the visual differences between siding types, along with their associated costs, is crucial for making informed decisions. This section provides detailed visual descriptions of three popular siding styles, exploring their aesthetic impact and cost implications.
The visual impact of your siding extends far beyond mere protection from the elements. It’s the first thing people see, setting the tone for your home’s entire aesthetic. Careful consideration of color, texture, and complementary architectural details can transform your house from ordinary to extraordinary.
Traditional Clapboard Siding
Traditional clapboard siding, characterized by its horizontal, overlapping planks, evokes a classic, timeless appeal. This style is often associated with New England charm and creates a sense of warmth and history. Typically made from wood, such as cedar or redwood, it offers a natural, textured finish. However, vinyl and fiber cement alternatives are also widely available, offering lower maintenance and varied price points. While wood clapboard can range from $8 to $15 per square foot installed, vinyl alternatives may cost between $4 and $10 per square foot, and fiber cement options typically fall between $10 and $20 per square foot. The price variation reflects the material’s durability, longevity, and aesthetic qualities. Imagine a charming colonial-style home, painted a soft, muted gray, with crisp white trim accentuating the windows and door frames. This classic combination exudes elegance and sophistication.
Modern Board and Batten Siding
Modern board and batten siding offers a clean, linear aesthetic, perfectly suited for contemporary or farmhouse-style homes. This style features wide vertical planks (the “battens”) covering narrower, horizontal boards. The stark vertical lines create a visually striking effect, lending a sense of modernity and sophistication. Materials commonly used include wood, fiber cement, and even metal. Wood options, like cedar or pine, offer a natural warmth, while fiber cement provides durability and low maintenance. Metal options provide a sleek, modern look with exceptional longevity. Cost-wise, expect to pay a slightly higher premium compared to traditional clapboard, with wood ranging from $12 to $20 per square foot, fiber cement from $15 to $25 per square foot, and metal options potentially exceeding $20 per square foot depending on the chosen material and finish. Picture a sleek, white board and batten home with black metal accents, a perfect example of clean lines and modern design.
Contemporary Metal Panel Siding
Contemporary metal panel siding represents a bold, modern aesthetic. Available in a wide array of colors and finishes, it provides a sleek, low-maintenance exterior. The panels can be installed horizontally or vertically, offering design flexibility. Metal siding is exceptionally durable and resistant to weather damage, making it a long-term investment. While the initial cost is generally higher than wood or vinyl, the longevity and low maintenance often offset the higher upfront investment. Prices typically range from $15 to $30 per square foot installed, varying based on the metal type (aluminum, steel, zinc) and finish. Visualize a striking home with deep charcoal gray metal siding, accented by sharp, geometric lines and large windows – a testament to modern architectural design. The clean lines and durable nature of the material contribute to a sense of sophistication and permanence.
Visual Impact of Siding Colors and Textures
The choice of siding color and texture significantly impacts the overall aesthetic. Light colors can make a house appear larger and brighter, while darker colors create a more dramatic and intimate feel. Textured siding, like wood clapboard or stone veneer, adds depth and visual interest, while smooth surfaces offer a more contemporary and minimalist look. Consider the surrounding landscape and architectural style when selecting colors and textures to ensure a cohesive and visually appealing design. For instance, a rustic home in a wooded area might benefit from earth-toned siding with a natural texture, while a modern home in a city setting might look best with sleek, smooth siding in a bold color.
Effect of Contrasting Trim and Architectural Details
Contrasting trim and architectural details, such as window casings, door surrounds, and fascia boards, significantly enhance the visual appeal of any siding project. These details add depth, definition, and visual interest, drawing the eye and creating a more polished and finished look. While strategically placed contrasting trim can elevate the aesthetic, it also increases the overall cost. For example, using high-quality, custom-milled trim in a contrasting color will be more expensive than using standard, pre-fabricated trim. However, the impact on the final visual result is often well worth the extra investment. A well-executed trim strategy can dramatically improve a home’s curb appeal and increase its perceived value.
Siding your house is a significant investment, impacting both your home’s curb appeal and its long-term value. By carefully considering the factors Artikeld in this guide—material choices, labor costs, regional variations, and your project’s complexity—you can create a realistic budget and choose the best siding option for your needs. Remember, thorough planning and research are key to a successful project that enhances your home’s beauty and protects it for years to come. Don’t let unexpected costs derail your dream; arm yourself with knowledge and confidently tackle your siding project.
Answers to Common Questions
Can I install siding myself to save money?
While possible, DIY siding installation is often more challenging than it seems. Professional installation ensures proper techniques, preventing future issues and potential damage. Weigh the time commitment, potential for mistakes, and the cost of tools against professional labor costs before deciding.
How long does siding installation typically take?
The timeframe varies based on house size, siding type, and complexity. Smaller projects might take a few days, while larger, more intricate jobs could extend to several weeks. Get a precise timeline from your contractor.
What about financing options for siding projects?
Many contractors offer financing plans, or you can explore home improvement loans through banks or credit unions. Compare interest rates and terms before committing to any financing option.
Does homeowner’s insurance cover siding damage?
Coverage depends on your policy and the cause of the damage. Windstorms, hail, and fire are often covered, but normal wear and tear usually isn’t. Review your policy details or contact your insurer for clarification.
How often should I expect to maintain my siding?
Maintenance requirements vary depending on the siding material. Vinyl typically needs minimal care, while wood requires regular cleaning and potential repainting. Your contractor can advise on a suitable maintenance schedule for your chosen siding.



